Creating your first variable
If you used the Kickstart Panel you'll already have a dummy variable created as an example.
Otherwise, your variables table will be empty.
IMPORTANT NOTE: If you have an
.envfile (or similar key=value text file) and you want to import that information (either just the variable names or both names and values), check out the importing .env files section down below.
Manually creating variables
Let's create your database username as a variable!
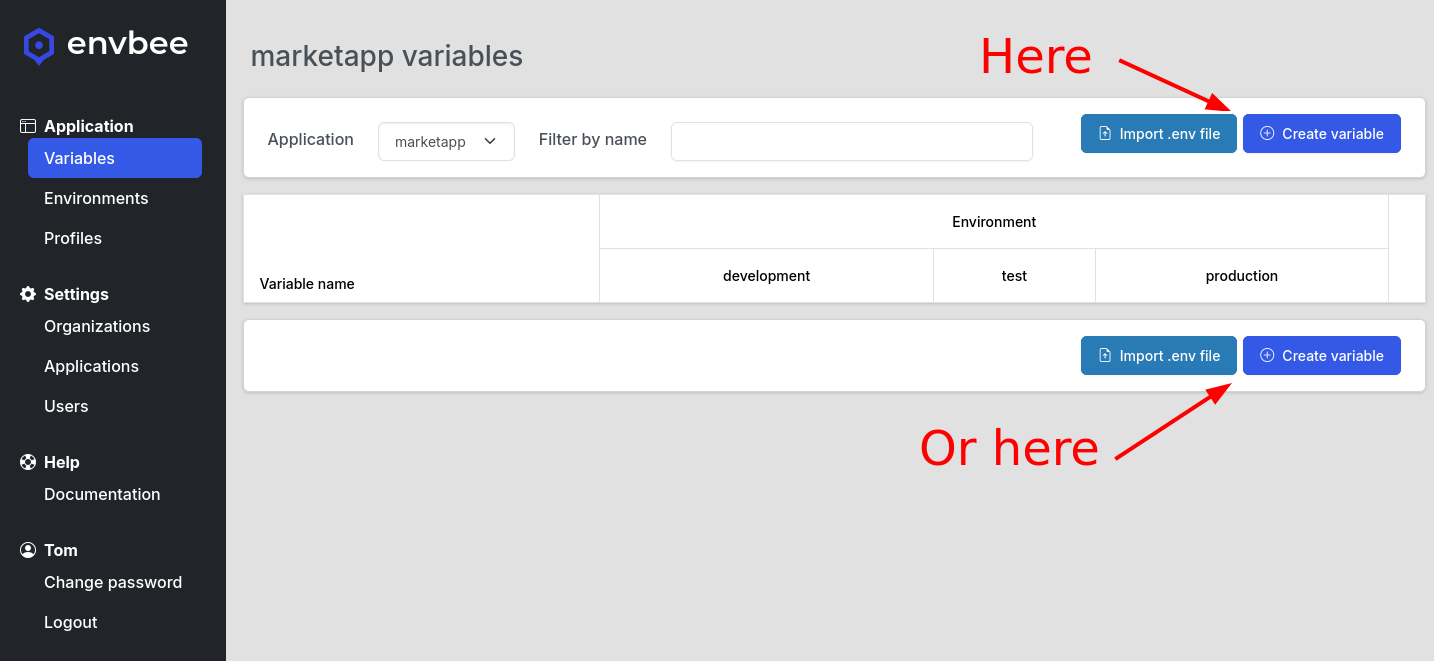
First, click on the Create variable button.
Then, type the name of your variable (we could use DATABASE_USERNAME here), choose a type (STRING is fine for this example).
You can write a description for your variable, but it's optional.
And you can already fill the variable values for each of the existing environments.
In our example, we'll complete all these values too.
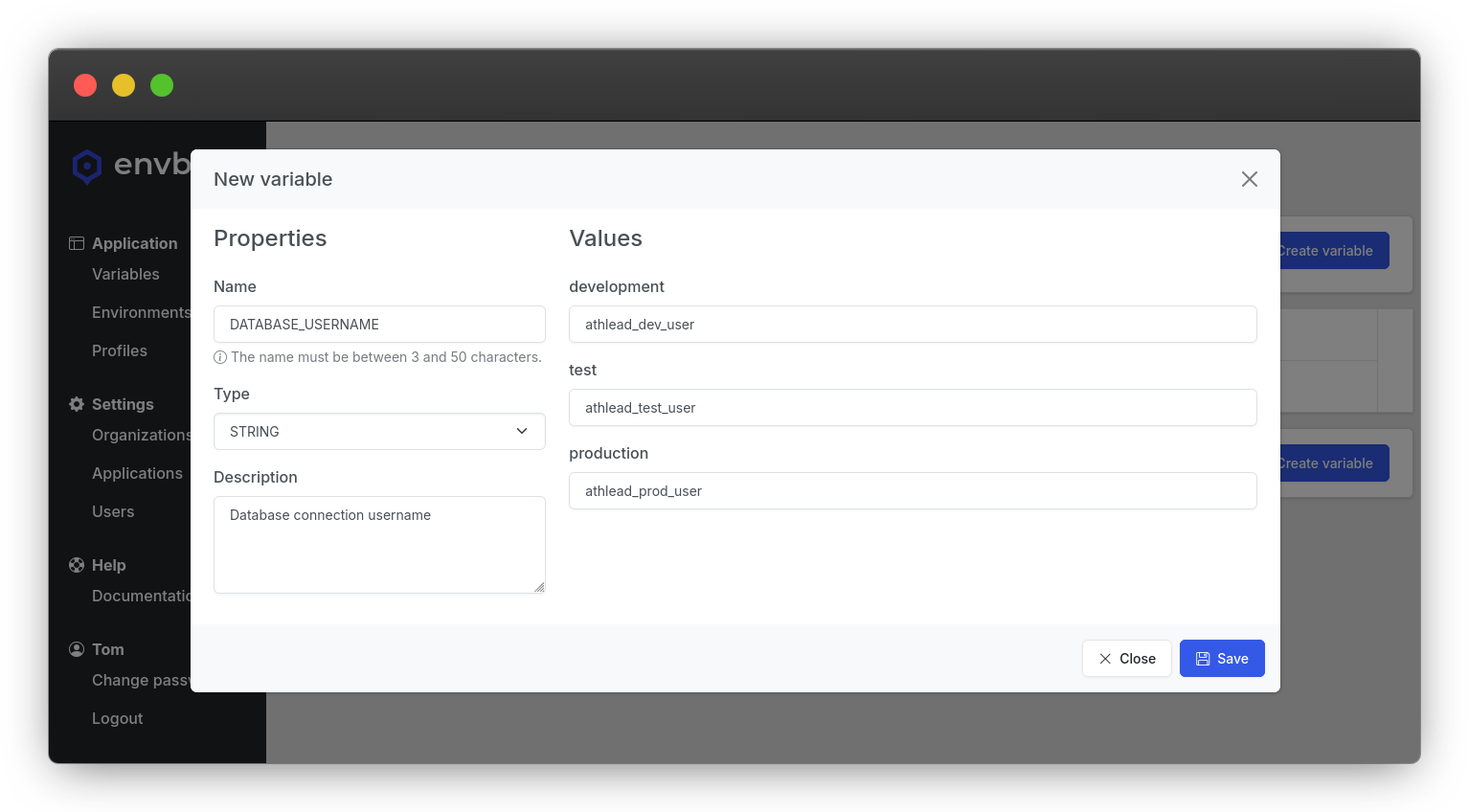
Once you're done, click on Save and you have your variable ready to be used.

Importing env files
If you have a text file with key=value pairs in it (usually these are .env files or .env.test, etc) you can import them into envbee.
This would be a valid .env file example to use here:
DATABASE_USERNAME=db-user
DATABASE_PASSWORD=db-pass
To import such a file, click on the Import .env file button.
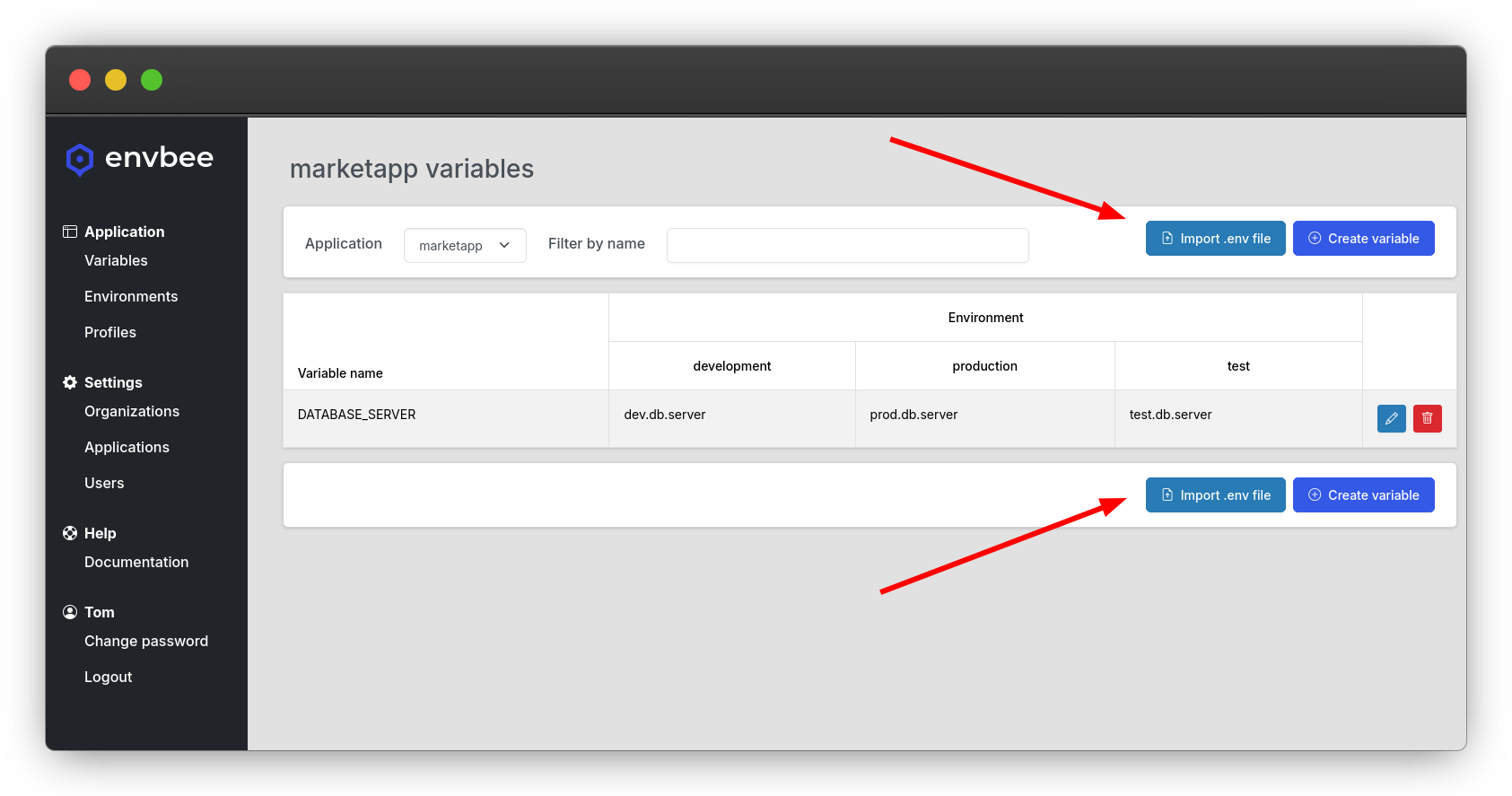
The first thing to do is selecting the file to upload.
After that, you can omit selecting any environment and the system will just create any variable that you don't already have in the system. This means that you can run this import multiple times and it will just add new variables.
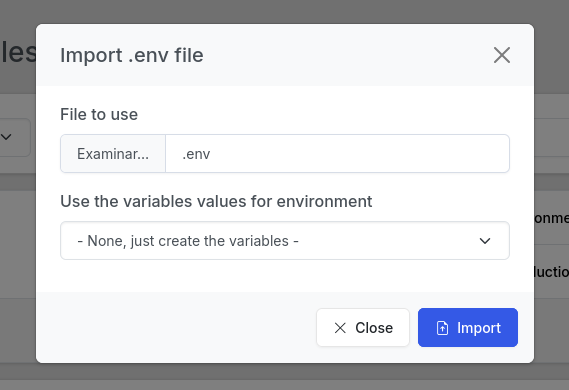
Or you can select an environment and envbee will use the values in your .env file to fill the variables values for that environment.
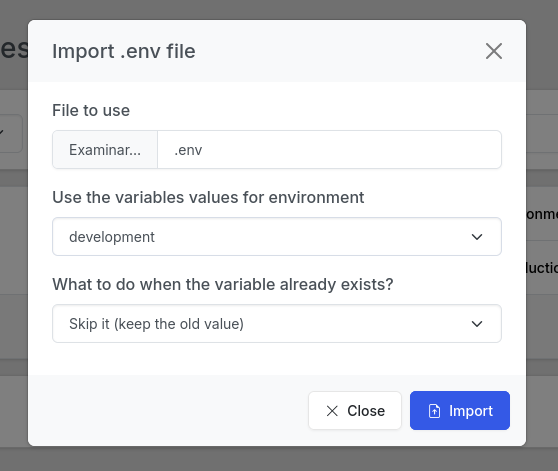
If you select an environment to fill the values, you can select if you want to overwrite the existing values or not.